Mosquitoes are more than just a nuisance; they are carriers of some of the world’s most dangerous diseases. According to the World Health Organization, mosquito-borne diseases account for several million deaths and hundreds of millions of cases every year. From Malaria to Zika, these tiny insects have a significant impact on global health. Understanding the diseases they carry, their symptoms, and prevention methods is crucial for both individual and community well-being. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to mosquito-borne diseases, their symptoms, and how to protect oneself effectively.
Contents
The Biology Of Mosquitoes
Mosquitoes are complex creatures with a unique anatomy that makes them efficient disease carriers. Their needle-like mouthparts, called proboscis, are designed to pierce the skin and draw blood, simultaneously injecting saliva that may contain pathogens. Understanding the biology of mosquitoes is the first step in comprehending how they transmit diseases.
Mosquitoes breed in stagnant water, making areas with poor water management high-risk zones for mosquito-borne diseases. From puddles to water-filled containers, these breeding grounds are often found close to human habitats. Eliminating these water sources can significantly reduce the mosquito population, thereby lowering the risk of disease transmission.
Common Mosquito-Borne Diseases
Malaria is perhaps the most well-known mosquito-borne disease, affecting millions of people worldwide. Transmitted through the Anopheles mosquito, Malaria is most prevalent in sub-Saharan Africa but is also found in parts of Asia and South America. Early symptoms include fever, chills, and headache, which can escalate to severe illness or death if not treated promptly.
Dengue Fever and Zika Virus are other common diseases spread by the Aedes mosquito. Dengue is prevalent in tropical and subtropical regions, causing high fever, severe headaches, and joint pain. Zika Virus gained global attention due to its potential to cause birth defects when pregnant women are infected. Both diseases currently have no specific treatment, making prevention crucial.
Lesser-Known Mosquito-Borne Diseases

While Malaria, Dengue, and Zika often make headlines, other lesser-known diseases like Yellow Fever and Chikungunya are also of concern. Yellow Fever is most common in parts of Africa and South America and can cause severe liver disease. Vaccination is available and is the most effective way to prevent infection.
Chikungunya, on the other hand, is found in Africa, Asia, and the Indian subcontinent. The disease causes fever and severe joint pain but is rarely fatal. West Nile Virus is another lesser-known disease primarily found in the United States. Unlike other mosquito-borne diseases, West Nile Virus can also affect birds and other animals, making it a unique concern for both public and animal health.
Symptoms to Watch For

Recognizing the symptoms of mosquito-borne diseases is crucial for timely medical intervention. Common symptoms across multiple diseases include fever, headache, and joint pain. In some cases, these symptoms may be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, or a rash. It’s essential to consult a healthcare provider if you experience these symptoms, especially after traveling to a high-risk area.
Knowing when to seek medical help can be a lifesaver. If symptoms persist or worsen, immediate medical attention is required. For diseases like Malaria, early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for a full recovery. Blood tests can confirm the presence of pathogens, and appropriate treatment can be administered based on the diagnosis.
Prevention Methods
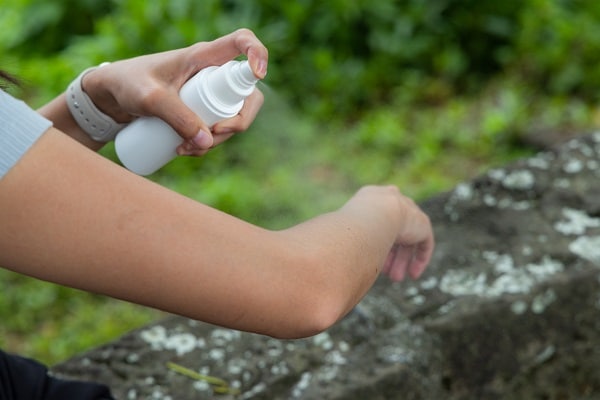

Chemical repellents containing DEET or Picaridin are often recommended for preventing mosquito bites. These chemicals work by confusing the mosquito’s sense of smell, making it harder for them to locate humans. However, it’s essential to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for application and reapplication to ensure maximum effectiveness.
Natural alternatives like citronella and lavender oils are also popular but may not be as effective as chemical repellents. Environmental control measures, such as eliminating stagnant water sources, can also help reduce the mosquito population. Community-wide efforts like fogging and larviciding can be effective but require coordinated action and resources.
Vaccines and Treatments
Vaccines for some mosquito-borne diseases like Yellow Fever are available and highly effective. For travelers visiting high-risk areas, vaccination is often recommended as a preventive measure. However, for diseases like Malaria and Dengue, no fully effective vaccine is currently available, although research is ongoing.
Several antiviral and antimalarial medications can treat mosquito-borne diseases, but early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Research into new treatments and vaccines is ongoing, with some promising candidates in clinical trials. However, prevention remains the most effective strategy until more comprehensive treatments are developed.
Global Initiatives to Combat Mosquito-Borne Diseases

International organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) have set guidelines for combating mosquito-borne diseases. These guidelines include recommendations for vector control, surveillance, and community engagement, aiming to reduce the global impact of these diseases.
Community-based programs have shown success in reducing the incidence of mosquito-borne diseases. For example, the use of insecticide-treated bed nets has significantly reduced Malaria cases in several African countries. Public awareness campaigns and education are also crucial components of these community efforts, empowering individuals to take preventive measures.
The Future of Mosquito-Borne Diseases
Climate change poses a significant threat to the spread of mosquito-borne diseases. Rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns can expand the habitats suitable for mosquitoes, potentially increasing the incidence of these diseases. Public health systems must adapt to these changing conditions to prevent outbreaks effectively.
Technological advancements offer hope in the fight against mosquito-borne diseases. From gene editing techniques aimed at reducing mosquito populations to new diagnostic tools for rapid disease detection, technology could play a crucial role in future prevention and treatment efforts.
The Bottom Line
Mosquito-borne diseases are a global health concern that requires concerted efforts for effective management and prevention. Understanding the biology of mosquitoes, recognizing the symptoms of the diseases they carry, and taking preventive measures are crucial steps in combating these deadly diseases. As research continues and technology advances, there is hope for more effective treatments and perhaps even cures. Until then, awareness and prevention remain our best defense.


